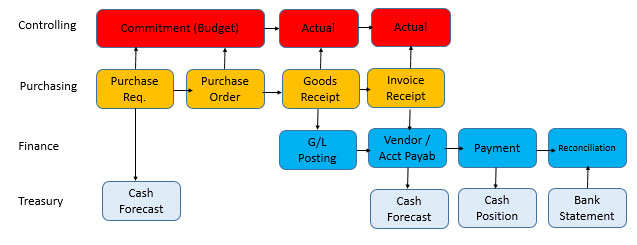
Real-time integration between finance and logistics has always been SAP’s trump card. SAP ERP collects and combines data from the separate modules. The quality of the integration rests on quality of the configurations, master data and skills of the users. The decisions in logistics influence finance and vice versa.
A successful SAP implementation requires understanding of configuration choices and their consequences. The training courses teach you how to assign company codes to companies, controlling areas, sales and purchase organizations, plants. In real life you will be sitting in hierarchy workshops trying to figure out how to get the SAP organization model to correspond the company’s own structures and needs?
Answers to these questions are not always easy. Many companies have made costly decisions in the history. These structures are not easy to change.
What is plant in finance? What is the difference between profit center and cost center? What are cost elements? Are all accounts cost elements? How to pass product costs to profitability analysis?
Understand the Integration between logistics and the FI and CO components
To what extent should finance people know the other modules? Should they know how goods and information flow through logistics? It is sufficient to recognize the integration points, where the accounts are determined. This is located in places where goods arrive or leave the company or the value of the goods changes. The better finance knows the logic of these processes and the configurations behind them, the better they can rely on the quality of the generated postings.